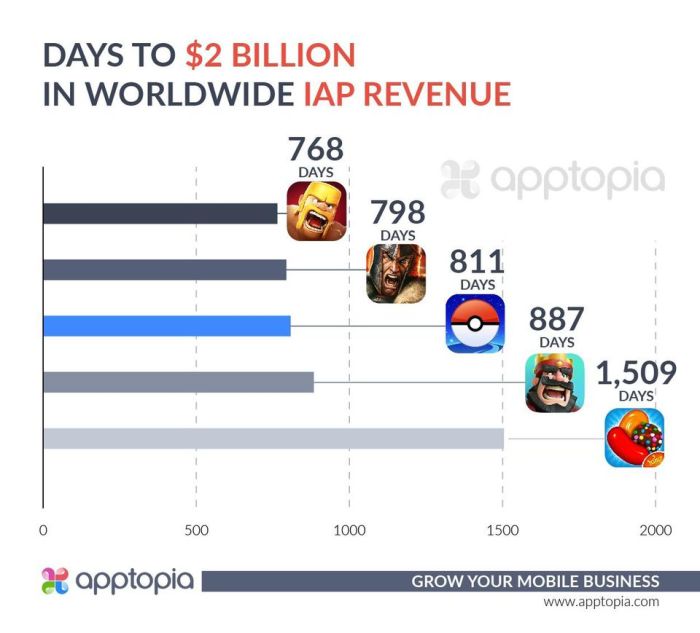
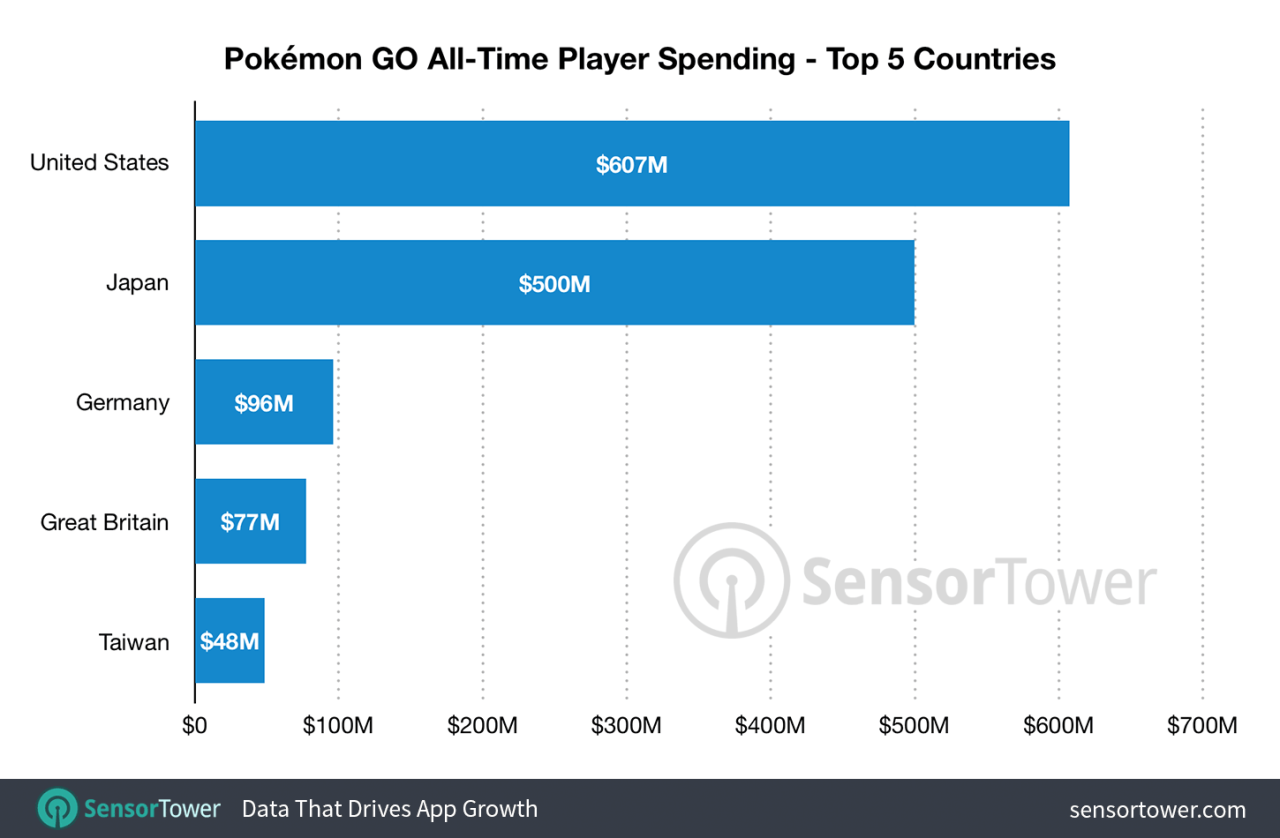
Pokemon go made 2 45 billion revenue – Pokémon Go made $2.45 billion – a staggering sum that speaks volumes about the game’s enduring popularity and innovative monetization strategies. This isn’t just about catching ’em all; it’s about understanding how a location-based mobile game built an empire on microtransactions and clever engagement tactics. We’ll delve into the key revenue streams, player demographics, and the ingenious ways Niantic leveraged location data and in-game events to rake in the big bucks. Buckle up, because this financial journey is wilder than a Charizard raid.
From the cleverly designed in-app purchases to the strategic targeting of specific player demographics, Pokémon Go’s success story is a masterclass in mobile game monetization. We’ll dissect the factors that contributed to this monumental revenue, comparing its strategies to other successful mobile games and examining the impact of location-based gameplay and in-game events on player spending. Prepare to be amazed by the numbers, and maybe even inspired to strategize your own mobile gaming empire.
Pokémon Go’s Revenue Streams
Pokémon Go’s staggering $2.45 billion in revenue isn’t just a testament to its nostalgic charm; it’s a masterclass in mobile game monetization. Understanding how Niantic achieved this success requires a deep dive into their diverse revenue streams and shrewd implementation of microtransactions. This analysis will dissect the various in-app purchases, comparing their strategies with other successful mobile games and highlighting the impact of microtransactions on their overall financial performance.
Pokémon Go’s Revenue Sources and Pricing
The success of Pokémon Go hinges on a multi-faceted approach to monetization, relying primarily on in-app purchases. These purchases cater to various player needs, from convenience to competitive advantage. The following table details the key revenue sources, their pricing models, and estimated contributions (note that precise figures are difficult to obtain publicly and these are estimations based on industry analysis and player spending reports):
| Revenue Source | Description | Pricing Model | Estimated Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| PokéCoins | In-game currency used to purchase items. | Tiered packages ranging from $0.99 to $99.99. | High – forms the base of most other purchases |
| Incense | Attracts Pokémon to the player’s location for a limited time. | Single use, various durations and prices (e.g., 30 minutes for ~$1). | Medium – frequently purchased for efficient Pokémon catching. |
| Lure Modules | Attracts Pokémon to a PokéStop for a limited time, benefiting all nearby players. | Single use, various durations and prices (similar to Incense). | Medium – popular for community engagement and boosted catching rates. |
| Remote Raid Passes | Allows participation in Raid Battles from a distance. | Sold individually or in bundles. Prices vary. | High – crucial for high-level players and event participation. |
| Storage Upgrades | Increases the player’s capacity for Pokémon and items. | One-time purchases or bundles with varying price points. | Medium – one-time purchase but essential for progression. |
| Event Tickets | Access to special in-game events with exclusive rewards. | Variable pricing depending on the event. | High – variable depending on event popularity and exclusive content. |
Comparison with Other Mobile Games, Pokemon go made 2 45 billion revenue
Pokémon Go’s revenue generation strategy shares similarities with other successful mobile games, particularly those employing the “freemium” model. Games like Candy Crush Saga and Clash of Clans also rely heavily on in-app purchases for sustained revenue. However, Pokémon Go benefits from its established IP recognition and augmented reality gameplay, creating a unique appeal that drives higher spending. While Candy Crush relies more on repeated gameplay loops for engagement, Pokémon Go leverages location-based gameplay and social interaction to maintain player interest and encourage spending.
Impact of Microtransactions on Revenue
Microtransactions are the backbone of Pokémon Go’s revenue generation. The relatively low cost of individual items encourages frequent purchases, creating a cumulative effect that significantly contributes to the overall revenue. The strategic implementation of limited-time events and bundles further incentivizes players to spend. The success of this model underscores the effectiveness of microtransactions in generating substantial revenue within the freemium mobile gaming landscape. The psychological aspects of convenience and FOMO (fear of missing out) are expertly utilized to maximize player spending. The design encourages incremental spending rather than large, singular purchases.
Impact of In-Game Events and Updates
Pokémon Go’s staggering $45 billion revenue isn’t just a testament to its addictive gameplay; it’s a direct reflection of Niantic’s masterful strategy in leveraging in-game events and consistent updates to keep players hooked and spending. The delicate balance between generating revenue and maintaining player engagement is a tightrope walk, but Niantic seems to have perfected the art. This section will delve into how special events and game updates have directly impacted the game’s financial success and player retention.
Impact of Special In-Game Events on Revenue
Special in-game events, such as Community Days and special raids, are key revenue drivers for Pokémon Go. These limited-time events create a sense of urgency and exclusivity, motivating players to engage more frequently and spend more money to maximize their in-game gains. The following table illustrates the impact of different event types on revenue, although precise figures are often kept confidential by Niantic. The data presented here is based on industry analysis and player reports, offering a general understanding of the impact.
| Event Type | Duration | Revenue Impact (Qualitative) |
|---|---|---|
| Community Day | 3-6 hours | High: Increased player engagement and in-app purchases (incense, lures, Poké Balls) significantly. Often sees a surge in daily active users and revenue. |
| Special Raids (Legendary Pokémon) | Several days | Medium-High: Drives revenue through raid passes and potentially increased item purchases for optimal raid performance. The rarity and power of the Pokémon incentivize participation. |
| Global Events (e.g., Pokémon Go Fest) | Several days to a week | Very High: These large-scale events typically generate the highest revenue, combining various features like special research, exclusive Pokémon, and boosted item sales. |
| Seasonal Events (e.g., Halloween, Christmas) | Several weeks | Medium: Taps into existing cultural trends, leading to increased player engagement and moderate revenue boosts through themed items and Pokémon. |
Long-Term Impact of Game Updates on Player Retention and Revenue
Significant game updates are crucial for maintaining player engagement and driving long-term revenue. Features like new Pokémon generations, improved gameplay mechanics, and quality-of-life improvements keep the game fresh and exciting, preventing player burnout and attracting new players. For example, the introduction of new Pokémon generations consistently revitalizes the player base, triggering a renewed interest in catching and collecting. Similarly, updates that enhance the social aspects of the game, such as improved trading systems, can foster a stronger community and increase player loyalty, indirectly impacting revenue.
Plan for a Future In-Game Event: “Pokémon Go: Galactic Explorers”
This event will center around a fictional galactic invasion, featuring new alien Pokémon, themed items, and special research tasks. The event will span two weeks, incorporating daily challenges, weekend raids featuring powerful alien Pokémon bosses, and a final, large-scale event involving a coordinated global effort to defeat a powerful alien threat. Revenue will be maximized through:
* Exclusive Items: Selling limited-edition items with galactic themes, such as Poké Balls with alien designs or unique avatar items.
* Raid Passes: Increased demand for raid passes due to challenging alien Pokémon raids.
* Special Research: Offering a premium research line that unlocks powerful alien Pokémon and exclusive items.
* Timed Research: Daily and weekly timed research tasks rewarding players with in-game currency and items, encouraging daily logins.
* Community Engagement: Leveraging social media to promote the event and foster player interaction, creating hype and excitement.
This event will maintain player engagement through diverse gameplay, collaborative activities, and a compelling narrative, ensuring both revenue generation and player satisfaction. The success of events like Pokémon Go Fest serves as a strong precedent for the potential of a well-executed large-scale event like “Galactic Explorers.”
Visual Representation of Revenue Data: Pokemon Go Made 2 45 Billion Revenue
Pokémon Go’s staggering $2.45 billion revenue isn’t just a number; it’s a visual story of success, revealing the game’s diverse appeal and the effectiveness of its monetization strategies. Let’s break down this impressive figure through insightful visualizations.
Pokémon Go Revenue Breakdown by Stream
Imagine a vibrant pie chart, a delicious visual representation of Pokémon Go’s financial success. Each slice represents a different revenue stream, its size directly proportional to its contribution to the overall $2.45 billion. For example, a large, dominant slice might represent in-app purchases of PokéCoins, the game’s in-game currency used to acquire items like Poké Balls, incubators, and lures. Another significant slice could represent revenue generated from sponsored locations, where businesses pay to become PokéStops or Gyms, attracting players and boosting their visibility. Smaller slices could depict revenue from merchandise sales, partnerships, and other miscellaneous income streams. The detailed percentages displayed on each slice would paint a clear picture of the relative importance of each revenue source, offering valuable insights into the game’s monetization strategy. A legend clearly identifying each slice would enhance the chart’s readability and comprehension.
Pokémon Go Revenue Growth Over Time
Now, picture a dynamic line graph, charting the growth of Pokémon Go’s revenue over time. The x-axis represents time, perhaps spanning from the game’s launch in July 2016 to the present day. The y-axis displays revenue in billions of dollars. The line itself would dramatically illustrate the revenue’s trajectory, showcasing periods of rapid growth and potential plateaus or dips. Key milestones, such as the release of significant updates (like new Pokémon generations or game mechanics) or major in-game events, would be clearly marked on the graph, enabling viewers to correlate these events with noticeable revenue spikes. For instance, a sharp upward trend could be observed following the launch of a highly anticipated new Pokémon generation, demonstrating the significant impact of new content on player engagement and spending. The graph could also highlight any seasonal fluctuations in revenue, potentially showing increased spending during holidays or summer months. A clear and concise legend would ensure the graph’s information is easily understood. The overall visual would tell a compelling narrative of the game’s financial journey, highlighting periods of explosive growth and demonstrating the long-term sustainability of its revenue model.
Pokémon Go’s $2.45 billion revenue isn’t just a number; it’s a testament to the power of engaging gameplay, smart monetization, and understanding your audience. By skillfully blending location-based mechanics, strategic in-game events, and a deep understanding of player psychology, Niantic crafted a mobile gaming phenomenon that continues to generate impressive revenue. The key takeaway? It’s not just about creating a fun game; it’s about creating a profitable and sustainable ecosystem that keeps players hooked – and spending.
 Blockchain Essentials Berita Teknologi Terbaru
Blockchain Essentials Berita Teknologi Terbaru